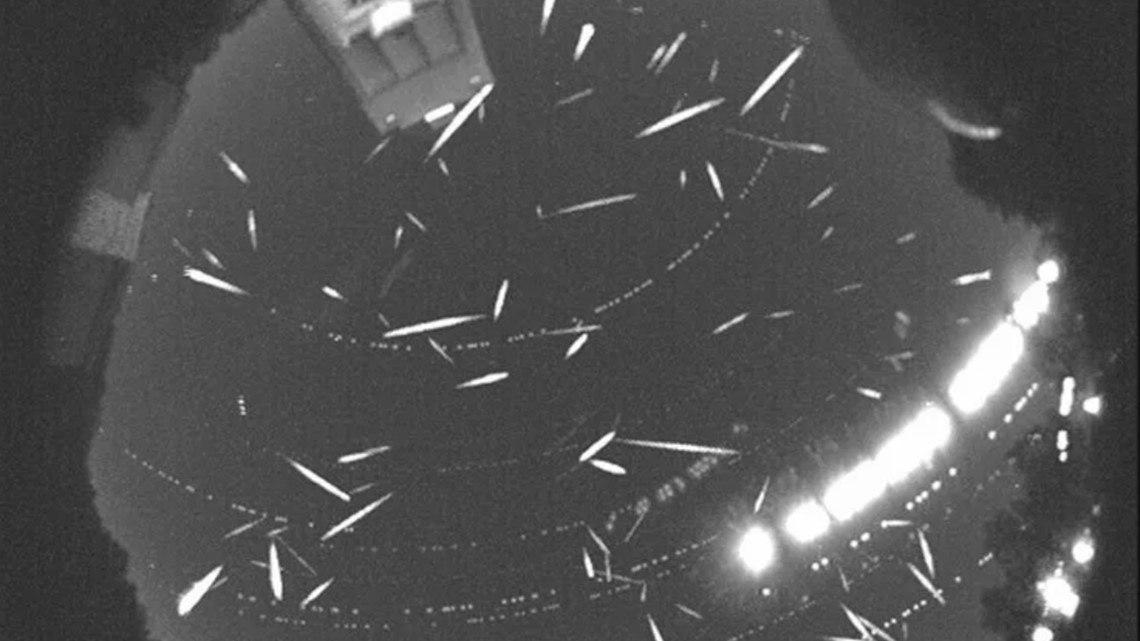
MOLINE, Ill — Attention skywatchers! Brace yourself for the most spectacular celestial show of the year, the Geminids meteor shower! This will be the biggest and brightest meteor shower of the year and it is set to peak on the nights of December 13th and 14th. This particular meteor shower is known for often leaving persistent trails in its wake along with a high rate of fireballs, which are even more noticeable.
A new moon brings an even better view
As a bonus this year, a new moon phase will be taking place on December 12th, very close to the peak of meteor shower activity. This means the night sky will be even more dark, providing great viewing conditions for the Geminids. Experts say that we can expect to see up to 120 meteors per hour streaking across the sky.
When, where, and how to watch
When: Wednesday, December 13th and Thursday, December 14th, anytime after 8 p.m. until dawn. The meteor shower will be most visible between midnight and 4 a.m. each day.
Where: All parts of the sky
How: Find a dark location that has very little in the way of light pollution. You won't want to be in or near the Quad Cities metro or any other large population center for that matter. That makes some of our smaller hometowns the perfect spot for viewing, especially in the country!


Give your eyes time to adjust to the darkness of the night sky, roughly 20 minutes or so. That will make it even easier to see the meteor action.
You'll also want to keep your Storm Track 8 App handy to monitor cloud cover trends. Times of clear sky are expected, but as always the app will show you where the thickest cloud cover is in real time.
You'll want to look at all parts of the sky, not just around the constellation Gemini.
Remember to dress warmly as forecast temperatures are expected to drop back into the 20s for several nights.
Where do meteors come from?
Meteors come from leftover comet particles and pieces of asteroids. When these objects rotate around the Sun, they leave a dusty trail behind. Every year Earth passes through these trails, which allows the pieces to collide with our atmosphere where they burn up and disintegrate to create firey and colorful streaks in the sky.